
In today’s customer experience (CX) landscape, speed, accuracy, and personalization are no longer optional—they are expected. AI-powered chatbots have emerged as one of the most effective tools to meet these expectations. At the heart of their effectiveness lies a single concept: intent recognition.
By identifying what a customer truly wants to achieve—whether it’s resetting a password, tracking an order, or expressing frustration—intent-driven chatbots transform fragmented conversations into seamless resolutions. This article explores what chatbot intents are, how they are applied across industries, and why they are becoming a critical driver of modern CX.
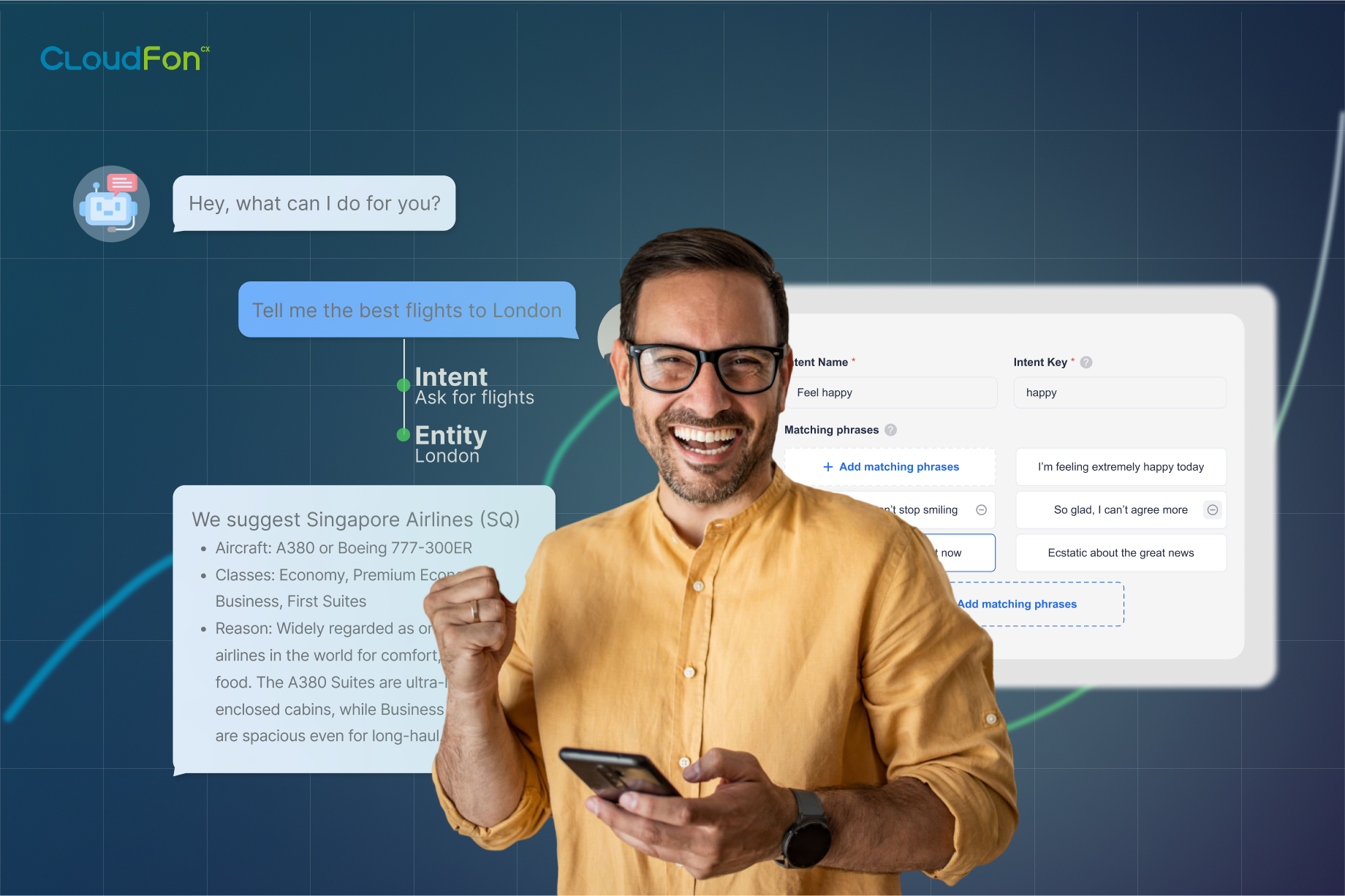
An intent is the underlying goal behind a user’s message. For example:
“I forgot my password”
“Can't log in”
“Reset my account”
Though phrased differently, each points to the same intent: password reset.
This abstraction allows AI chatbots to move beyond keyword matching and instead focus on resolving the customer’s actual need. Intents are the building blocks of meaningful automation and the foundation of conversational AI.

Intent-driven chatbots are not confined to a single industry—they deliver value wherever organizations interact with customers. By shifting from manual processes to automated intent recognition, businesses reduce friction, improve satisfaction, and scale service efficiently.
Before: Customers waited in queues, navigating IVR menus or repeating their problem to multiple agents.
After: Typing “I can’t log in” instantly triggers the reset password intent, resolving the issue within seconds.
Industry Examples:
Banking & Finance – login issues for mobile banking apps.
Telecommunications – SIM activation or network troubleshooting.
E-commerce – quick account recovery before checkout.
Before: Shoppers relied on static product pages or waited for a salesperson to answer basic queries.
After: Asking “Show me laptops under $1,000” or “Find eco-friendly detergents” is mapped to a product recommendation intent, with the chatbot presenting curated options and guiding checkout.
Industry Examples:
Retail & E-commerce – faster product discovery and cross-sell suggestions.
Hospitality & Travel – recommending packages (e.g., “Find a family resort in Bali”).
Consumer Electronics – guiding buyers by price, features, or brand.
Before: Routine actions like rescheduling a flight or canceling an order required long customer service calls.
After: Chatbots process requests such as “Reschedule my flight to tomorrow” in real time, escalating to a live agent only when exceptions arise.
Industry Examples:
Airlines & Travel – flight changes, booking upgrades, cancellations.
Healthcare – scheduling, rescheduling, or canceling appointments.
Logistics – initiating product returns or changing delivery slots.
Before: Customers searched through confirmation emails or waited for human assistance.
After: Queries like “Where’s my package?” or “What’s my balance?” map to an information intent, with the chatbot fetching data instantly.
Industry Examples:
E-commerce & Logistics – package tracking and delivery status.
Banking & Insurance – balance checks, policy overviews, claim status.
Public Services & Utilities – bill inquiries, outage updates, due dates.
Before: Early chatbots could only handle transactions, leaving customers frustrated when expressing emotions like “I’m upset about this.”
After: Modern AI identifies emotional intents, responds empathetically, and escalates to a live agent when human care is required.
Industry Examples:
Healthcare & Wellness – guiding patients with empathy before connecting them to specialists.
Telecommunications – diffusing frustration during service outages.
Hospitality – acknowledging guest concerns in a natural, human-like manner.
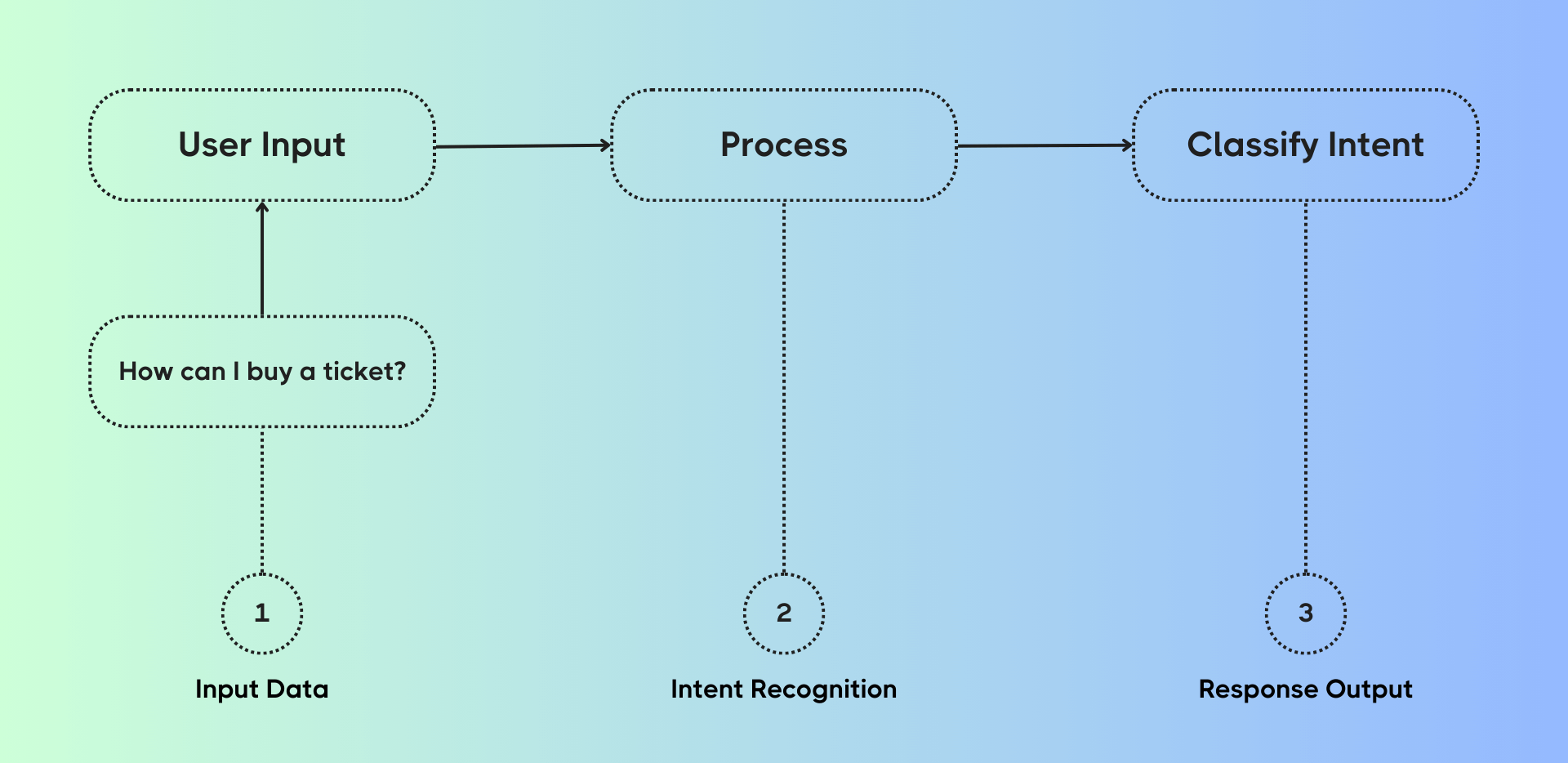
While industries vary, intents are broadly classified into four groups:
Informational – retrieving knowledge (e.g., “What’s your refund policy?”).
Transactional – completing an action (e.g., “Cancel my subscription”).
Navigational – moving to a specific resource or channel (e.g., “Connect me to billing”).
Conversational/Emotional – engaging in human-like dialogue (e.g., “I’m really frustrated right now”).
This classification provides a framework for designing scalable, intelligent chatbot systems.
Intent-driven automation impacts CX in measurable ways:
Reduced Friction – customers resolve issues faster, with fewer steps.
Personalization at Scale – responses tailored to context, history, and channel.
Operational Efficiency – fewer repetitive cases for agents, enabling focus on complex inquiries.
Consistent Service – intents apply across channels (voice, chat, social), ensuring reliability and brand consistency.
Customers – enjoy seamless, intuitive journeys without repeating information.
Agents – handle fewer routine questions and focus on higher-value cases, supported by pre-classified queries.
Supervisors & Managers – gain visibility into recurring issues and customer needs through intent analytics.
Enterprises – achieve cost optimization, operational agility, and stronger brand trust.
AI chatbot intents are no longer optional—they are the backbone of modern CX. By accurately mapping what customers mean to the right action, businesses not only save time and cost but also deliver the kind of responsive, empathetic service that builds loyalty.
From retail to healthcare, travel to finance, intent recognition is transforming customer interactions from reactive to proactive. Companies that invest in robust intent design and continuous refinement will not only keep pace with customer expectations but set new standards for digital engagement.